Abstract: Despite the crucial role insurance plays in mitigating risks for startups, the Nepalese insurance regulator and the insurance industry have yet to introduce transformative innovations such as digital-first and on-demand insurance, AI and data-driven underwriting, embedded insurance, blockchain and smart contracts, autonomous vehicle and drone insurance, and sandbox regulations. The Nepal Insurance Authority needs to formulate an insurance policy that supports startups and expedite the launch of an Insurtech Sandbox to foster greater startup growth in Nepal.
# Insurtech Startups in Neighboring Country
Insurance industry plays a crucial role in mitigating risks for startups, particularly in the Insurtech and broader entrepreneurial ecosystem. Innovation in the insurance industry, particularly by startups, is disrupting traditional models through technology, customer-centric approaches, and new risk management solutions. Here are some key areas where Insurtech startups are driving innovation neighboring country:
1. Digital-First & On-Demand Insurance
- Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): Startups like Metromile (pay-per-mile auto insurance) and Trov (on-demand coverage for gadgets) offer flexible, usage-based policies.
- Microinsurance: Companies like BIMA provide affordable, bite-sized insurance for low-income populations via mobile.
2. AI & Data-Driven Underwriting
- AI-Powered Risk Assessment: Startups like Lemonade use AI chatbots (Maya and Jim) for instant underwriting and claims processing.
- Alternative Data: Companies like Zesty.ai leverage satellite imagery and IoT data for property risk assessment.
3. Embedded Insurance
- API-Driven Insurance: Startups like Cover Genius enable e-commerce platforms (e.g., Shopify, Airbnb) to embed insurance at checkout (e.g., travel, gadget protection).
- Auto-Embedded Insurance: Tesla and Root Insurance integrate telematics to offer real-time, behaviour-based premiums.
4. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) & Community Insurance
- P2P Models: Startups like Teambrella and Friendsurance allow groups to pool risk and reduce fraud.
- Parametric Insurance: Etherisc (blockchain-based) automates payouts for flight delays or natural disasters.
5. Blockchain & Smart Contracts
- Fraud Reduction: Startups like Insurwave (marine insurance) use blockchain for transparent clFFaims.
- Decentralised Insurance (DeFi): Nexus Mutual offers smart contract-based coverage for crypto risks.
6. Cyber Insurance for SMEs & Individuals
- Startups like Cowbell Cyber and Corvus use AI to dynamically price cyber risks for small businesses.
7. Health & Wellness-Linked Insurance
- Wearable Integration: Vitality rewards healthy behaviour with discounts.
- Mental Health Coverage: Startups like Oscar Health integrate telehealth and wellness programmes.
8. Climate & Parametric Insurance for Emerging Risks
- Climate Risk Models: Kettle (AI for wildfire risk) and Raincoat (hurricane insurance in LatAm) offer fast parametric payouts.
9. Autonomous Vehicle & Drone Insurance
- Startups like Koop Technologies specialise in robotics and autonomous system coverage.
10. No-Code & Low-Code Insurance Platforms
- Companies like Boost Insurance allow anyone to launch an insurance product without heavy infrastructure.
# How regulators and the industry can support startups
Given the evolving nature of startups and the insurance sector in Nepal, risk mitigation involves regulatory frameworks, industry collaboration, and innovative insurance products. Nepali insurtech startups often face challenges like regulatory hurdles, customer trust in digital only models and high customer acquisition costs. Overcoming the challenges, here’s how regulators and the industry can support startups:
1. Regulatory Framework for Startup Protection
Insurance Board of Nepal (NIA) – The primary regulator can introduce policies to safeguard startups:
- Sandbox Regulations: Allow Insurtech startups to test innovative products under relaxed regulatory conditions (similar to India’s IRDAI sandbox).
- Simplified Compliance: Reduce bureaucratic hurdles for microinsurance and digital insurance providers.
- Mandatory Risk Coverage: Encourage (or mandate) basic business insurance for startups (e.g., fire, liability, cyber).
2. Industry-Led Risk Mitigation Measures
- Develop Startup-Specific Products:
– Business Interruption Insurance – Covers losses from disruptions (e.g., strikes, supply chain issues).
– Microinsurance for SMEs – Affordable policies for small businesses.
– Cyber Insurance – Protects against digital fraud and data breaches (critical for fintech startups).
- l Partnerships with Insurtech: Collaborate with startups for digital distribution (e.g., mobile-based policies).
3. Financial Risk Mitigation
- Credit Guarantee Schemes: Regulators can work with banks/NBFIs to insure startup loans (reducing lender risk).
- Parametric Insurance for Agriculture Startups: Weather-indexed crop insurance for agritech firms.
4. Disaster & Operational Risk Coverage
- Earthquake & Flood Insurance: Nepal is prone to natural disasters; startups need affordable catastrophe coverage.
- Supply Chain Insurance: For e-commerce/logistics startups facing delivery risks.
5. Cybersecurity & Fraud Prevention
- Regulator-Backed Cyber Risk Guidelines: Mandate basic cybersecurity compliance for fintech/Insurtech startups.
- Fraud Detection Partnerships: Insurers can integrate AI-driven fraud analytics for startups.
6. Awareness & Capacity Building
l Workshops on Risk Management: NIA and insurers should educate startups on insurance needs.
l Incubator Tie-Ups: Partner with hubs like NABIL Bank’s Startup Hub to offer tailored insurance packages.
# Why Nepal’s Insurance Authority (NIA) Should Launch an Insurtech Sandbox (Like Bangladesh’s IDRA)
An Insurtech sandbox is a regulatory framework that allows startups and insurers to test innovative insurance products, technologies, and business models in a controlled environment with relaxed rules. Bangladesh’s Insurance Development and Regulatory Authority (IDRA) launched its sandbox in 2021, which has helped foster digital insurance innovation.
Here’s why Nepal’s Insurance Board of Nepal (NIA) should implement a similar sandbox and how it could work:
1. Benefits of an Insurtech Sandbox in Nepal
A. Encourages Innovation in a High-Risk-Averse Market
-Nepal’s insurance sector is traditional and slow to adopt digital solutions.
-Startups hesitate to enter due to strict compliance burdens.
-A sandbox allows them to experiment without full regulatory penalties.
B. Attracts Insurtech Startups & Investment
-Foreign and local investors are more likely to fund startups if regulatory risks are reduced.
-Example: Bangladesh’s IDRA sandbox led to new digital insurers like Green Delta’s “Ignite”.
C. Protects Consumers While Allowing Testing
-Startups can pilot products with a limited number of users before full-scale rollout.
-NIA can monitor risks and shut down harmful experiments early.
D. Helps Regulators Understand New Technologies
-NIA can study blockchain, AI, and IoT in insurance before making permanent laws.
-Prevents regulatory lag (where laws struggle to keep up with tech).
2. How Nepal’s Insurtech Sandbox Could Work
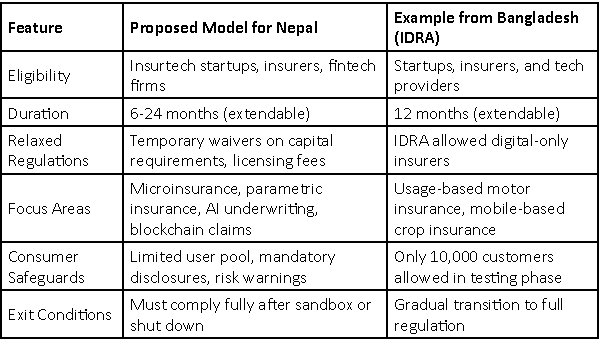
3. Which Startups & Innovations Could Benefit?
Nepali Insurtech startups could test:
✔ AI-Powered Claims Processing – Faster payouts for auto/health insurance.
✔ Blockchain for Fraud Prevention – Tamper-proof policies (like Etherisc).
✔ Microinsurance via Mobile Wallets – Partnerships with eSewa, Khalti.
✔ Parametric Weather Insurance – Instant payouts for farmers (e.g., drought/flood triggers).
✔ Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Insurance – Community-based risk-sharing models.
4. Steps for NIA to Launch the Sandbox
✔ Draft Sandbox Guidelines (Learn from IDRA, RBI India, MAS Singapore).
✔ Set Up a Dedicated Sandbox Team – Regulators, tech experts, and insurers.
✔ Open Applications – Startups submit proposals for testing.
✔ Monitor & Evaluate – Regular reporting to ensure consumer protection.
✔ Gradual Scaling – Successful pilots get full regulatory approval.
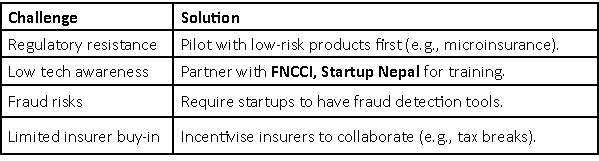
5. Challenges & Mitigations

(Views presented here are authors personal opinion and does not reflect the views of the Nepal Insurance Authority)